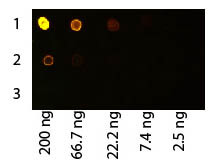
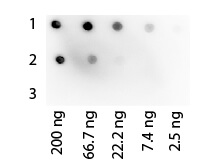
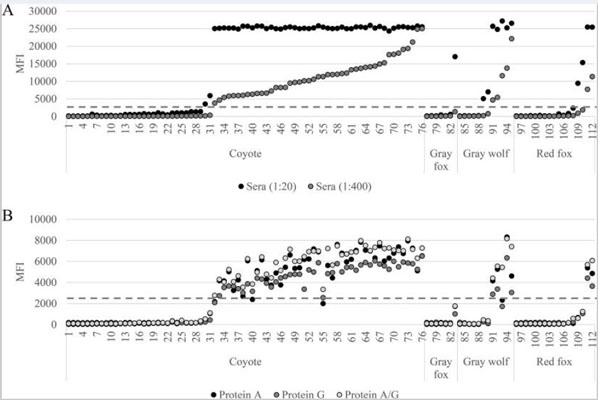
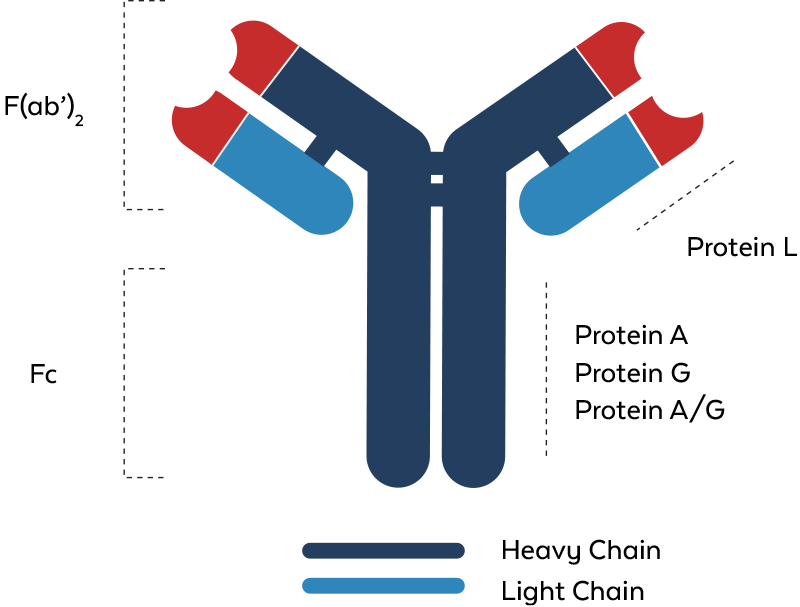
Protein A and Protein G are bacterial proteins renowned for their ability to bind to the Fc region of antibodies, particularly immunoglobulin G (IgG). Originating from Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcal bacteria respectively, these proteins are pivotal in the field of immunology and biotechnology for antibody purification and detection. Protein A/G is a recombinant protein that combines the IgG binding profiles of both Protein A and Protein G, offering a broadened specificity across various species and subclasses of IgG. This versatility makes Protein A, Protein G, and Protein A/G indispensable tools in biochemical research for their utility in various assays and purification processes.
Applications in IP and IgG Purification
Immunoprecipitation (IP) and IgG purification are key techniques in molecular biology that leverage the binding specificities of Protein A, Protein G, and Protein A/G. In IP, these proteins, often immobilized on a solid support, are used to isolate a specific antigen from a mixture by binding to a corresponding antibody. This allows for the study of protein-protein interactions, post-translational modifications, and protein function. In IgG purification, these proteins facilitate the selective extraction of IgG antibodies from complex samples, such as serum or cell culture media, by binding to the Fc region of IgGs. This purification is critical for producing high-purity antibodies for therapeutic use, diagnostics, and research applications.
Antibody Binding Properties
Below is a simplified overview of the antibody binding properties of Protein A, Protein G, and Protein A/G. Note that the actual binding strength (affinity) can vary based on several factors, including pH, ionic strength of the buffer, and specific protein variants.
| Species/Ig Subclass | Protein A | Protein G | Protein A/G |
| Bovine | |||
| IgG | |||
| IgG1 | |||
| IgG2 | |||
| Cat | |||
| IgG | |||
| Chicken | |||
| IgY | |||
| Dog | |||
| IgG | |||
| IgA (some) | - | ||
| IgM (some) | - | ||
| Donkey | |||
| IgG | |||
| Goat | |||
| IgG | |||
| IgG1 | |||
| IgG2 | |||
| Guinea Pig | |||
| IgG | |||
| IgG1 | - | ||
| IgG2 | - | ||
| Hamster | |||
| IgG | - | ||
| Horse | |||
| IgG | |||
| IgG (ab) | |||
| IgG (c) | |||
| IgG (T) | |||
| Human | |||
| IgG | |||
| IgA | |||
| IgA1 | |||
| IgA2 | - | ||
| IgD | |||
| IgE | |||
| IgG1 | |||
| IgG2 | |||
| IgG3 | |||
| IgG4 | |||
| IgM (some) | |||
| Monkey (Rhesus) | |||
| IgG | |||
| Mouse | |||
| IgG | |||
| IgG1 | |||
| IgG2a | |||
| IgG2b | |||
| IgG3 | |||
| IgM | |||
| Rabbit | |||
| IgG | |||
| Rat | |||
| IgG | |||
| IgG1 | |||
| IgG2a | |||
| IgG2b | |||
| IgG2c | |||
| Sheep | |||
| IgG | |||
| IgG1 | |||
| IgG2 |
Protein A
Protein A (UniProt P38507) is a 56 kDa protein from Staphylococcus aureus, featuring five Ig-binding domains that recognize the Fc fragment of IgGs across a range of mammalian species. The affinity of Protein A for IgG varies with the species and subclasses, allowing for tailored applications in purification. It is often conjugated to solid supports like Sepharose™, magnetic particles, or latex for efficient IgG purification from various biological samples.
Protein A and Conjugates
Protein G
Protein G (UniProt P19909, 63 kDa) binds a broader range of IgG subclasses compared to Protein A and has been modified in recombinant forms to eliminate albumin binding, enhancing its specificity for IgG. Similar to Protein A, Protein G conjugates are used extensively for the purification and detection of immunoglobulins, making it a versatile tool in biochemical and immunological research.
Protein G and Conjugates
Protein A and Protein G Sepharose™
Rockland's Protein A, Protein G, and Protein A/G Sepharose™ products are engineered for high-purity separation of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies. These fast-flow, low-leakage affinity resins are designed for efficiency and scalability in both laboratory and process-scale applications. Each lot undergoes rigorous quality control, including human IgG binding assays, to ensure optimal performance and reliability in antibody purification processes.