The neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) is crucial for regulating the serum half-life of IgG and albumin by rescuing them from lysosomal degradation and facilitating their recycling. The development of specific monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) against human FcRn (hFcRn) has significant therapeutic potential, particularly for autoimmune disease research and enhancing the pharmacokinetics of IgG-based therapeutics. Rockland and antibodies-online are proud to offer exclusive access to the anti-FcRn antibody clones ADM31 and DVN24 provided by Jackson Labs, ensuring unmatched quality and availability.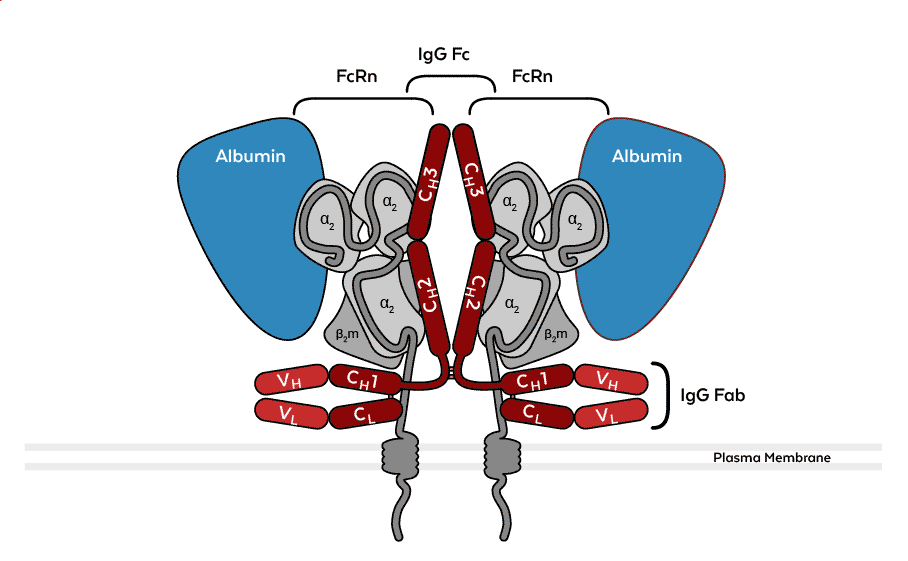
Figure. Binding of albumin (blue) and IgG (red) to the FcRn-β2m heterodimer based on the PDB structure 4N0U. Under mildly acidic conditions, glutamate and aspartate residues in the CH2 and CH3 domains of an IgG Fc fragment form hydrogen bonds with histidine residues in the α2 domains of two FcRn molecules. Albumin binds via its DIII and DI domains at a 1:1 stoichiometry to FcRn in a different region. Antibody blocking assays suggest that anti-FcRn antibody clone ADM31 binds to the FcRn-β2m heterodimer within the albumin binding region, whereas clone DVN24 blocks IgG binding.
Monoclonal Antibody Generation
Monoclonal antibodies against hFcRn were generated through immunization of mice with splenocytes from hFcRn-transgenic mice, followed by hybridoma technology. Supernatants from hybridomas were screened for binding activity to hFcRn using 293hFcRn-GFP cells in an ELISA. Clones showing activity were subcloned to ensure stable antibody production, resulting in nine unique hybridoma clones, including DVN24 and ADM31 (See Christianson et al., 2012 for details).
Features of DVN24
- Binding Specificity: DVN24 binds specifically to hFcRn and exhibits cross-reactivity with mouse FcRn (mFcRn).
- Epitope Specificity: Identified unique epitopes on hFcRn, demonstrating high affinity.
- Functional Activity: Potently blocks hIgG binding to hFcRn at low concentrations (3 μg/mL). In vivo, DVN24 accelerates the clearance of hIgG in hFcRn transgenic mice, demonstrating its potential for therapeutic applications to reduce pathogenic IgG levels in autoimmune diseases.
- Blocking Efficiency: DVN24 showed a significant reduction in serum hIgG concentrations without affecting human serum albumin (HSA) clearance, indicating specific blockade of the IgG binding site on hFcRn.
Features of ADM31
- Binding Specificity: ADM31 binds specifically to hFcRn without cross-reactivity to mFcRn.
- Epitope Specificity: Competes with DVN1 and ADM32 for binding sites, suggesting overlapping epitopes.
- Functional Activity: Selectively blocks HSA binding to hFcRn while leaving IgG binding intact.
- Tissue Distribution: ADM31 effectively detects hFcRn in tissue sections, particularly in the kidney, consistent with known FcRn expression patterns. This utility makes ADM31 a valuable tool for studying FcRn biology in various tissues.
At a Glance
| Clone | Isotype | Specificity | Applications | hIgG | HSA | mIgG |
| DVN24 | IgG2a | Human, Mouse | FC, IF, ELISA | + | - | + |
| ADM31 | IgG2b | Human | FC, IF, ELISA | - | + | - |
Both antibody clones are exclusively produced and sold through Rockland and antibodies-online. They are instrumental in studying FcRn functions, particularly in the context of autoimmune diseases and therapeutic antibody design. By targeting different binding sites on FcRn, they provide tools to dissect the distinct roles of albumin and IgG interactions with this receptor. This can lead to advancements in therapies that require modulation of antibody and protein half-lives in the bloodstream, enhancing the efficacy and stability of therapeutic proteins.