What Are Collagens? Understanding the Basics
Collagens are essential components of the extracellular matrix and continue to be important targets for technology and therapy. As the chief structural component of skin, collagen is the most abundant protein in the body, representing approximately 30% of its dry weight. The use of collagen has become increasingly prevalent in various medical applications such as implants, organ replacement, tissue equivalents, arterial plugs, cosmetic surgery, surgical sutures, and surgical dressings for wounds and burns. These advances were predicated on the use of anti-collagen antibodies to allow researchers to detect collagens, including type-specific collagens, in cell biology research.
Illustration depicting the triple helical structure of collagen
Variations in collagen structure create functional diversity essential for distinct biological features in the various types of tissues of the body. Based on their supramolecular structures, collagens are divided into two main classes: fibril-forming collagens (type I, II, III, and V) and non-fibril-forming collagens (type IV and VI). In humans, there are more than 20 unique procollagens that are subjected to various post-translational modifications resulting in great diversity between collagen types.
Collagen Antibodies
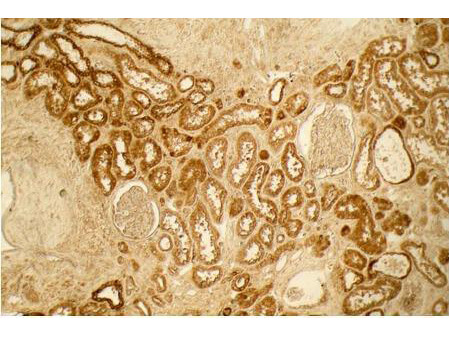
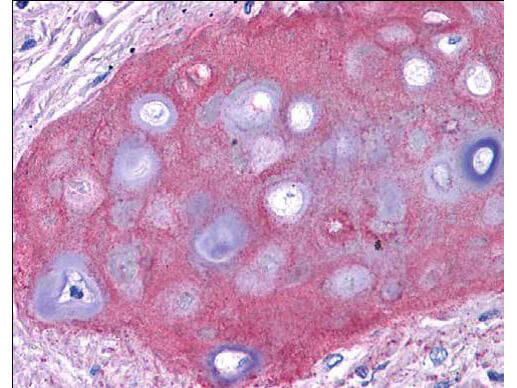
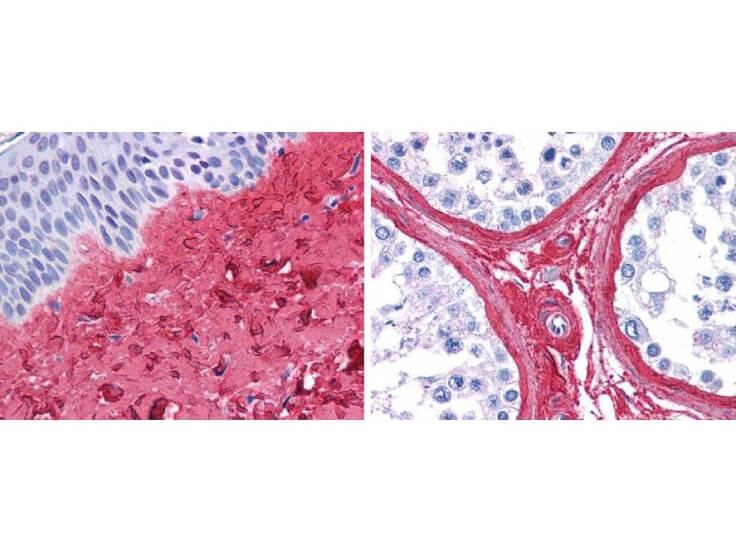
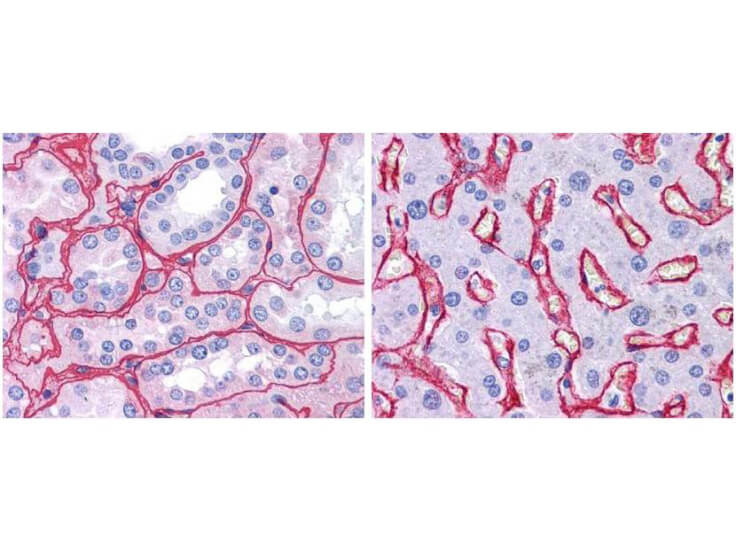
Precise insights into the behavior and physiology of cells can be made by researchers, especially when using a type-specific collagen antibody to study collagen’s bio-distribution, interactions between associated cells, mechanisms of cell adhesion, and cell development and differentiation. Because of the high specificity of type-specific anti-collagen antibodies, which often differentiate one collagen type from another by subtle differences in the triple-helical structure of native collagen molecules, it is important to select the correct antibody that is “fit-for-purpose” to detect a specific type of collagen in the right tissue and immunoassay. Rocklands collagen antibodies have been cited in more than 300 research publications, establishing them as the preferred option in nearly every circumstance when it comes to collagen research.
Type-Specific Collagen Antibodies
| Product | Clonality | Reactivity | Applications |
| Collagen Type I Antibody | Polyclonal | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Pig | WB, IHC, IF, FC, IP, Multiplex, ELISA |
| Collagen Type II Antibody | Polyclonal | Human, Bovine | IHC, IF |
| Collagen Type III Antibody | Polyclonal | Human, Bovine, Pig | WB, IHC, IF, FC, ELISA |
| Collagen Type IV Antibody | Polyclonal | Human, Bovine | WB, IHC, IF, Multiplex |
| Collagen Type V Antibody | Polyclonal | Human, Bovine | IHC, IF, Multiplex |
| Collagen Type VI Antibody | Polyclonal | Human, Bovine | IHC, IF |
Top Cited Collagen Antibodies
Frequently Asked Questions