Since their inception in 1978, nucleic acid therapies, including oligonucleotide therapeutics (ONTs) and vaccines, have expanded rapidly, particularly after the full approval of the first mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in 2021. ONTs now represent the third major class of drugs after small molecules and antibodies, with numerous recent approvals and ongoing clinical trials. These short nucleic acid fragments, such as antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) and small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), regulate gene expression by modulating RNA processing.
Despite their promise, ONT development faces significant challenges, including instability in biological fluids, inefficient cellular uptake, off-target effects, and immunogenicity. Regulatory agencies, such as the FDA, emphasize the need for improved bioanalytical tools to assess ONT pharmacokinetics, immunogenicity, and safety. We hypothesize that immunoassays, particularly those leveraging highly specific antibodies against ONTs, could help address these analytical gaps.
Antibodies Specific for Modification Independent of ONT Sequence
Using a targeted immunological approach, we developed and validated monoclonal antibody reagents that detect PS, 2′-MOE, and 2′-OMe modifications independent of nucleic acid sequence. These universal detection tools enable precise localization and quantification across various analytical methods, including immunofluorescence for intracellular sequestration (Fig. 1, 2), and quantification assays (Fig. 3). These data support their effectiveness as detection and quantification reagents in diverse experimental settings.
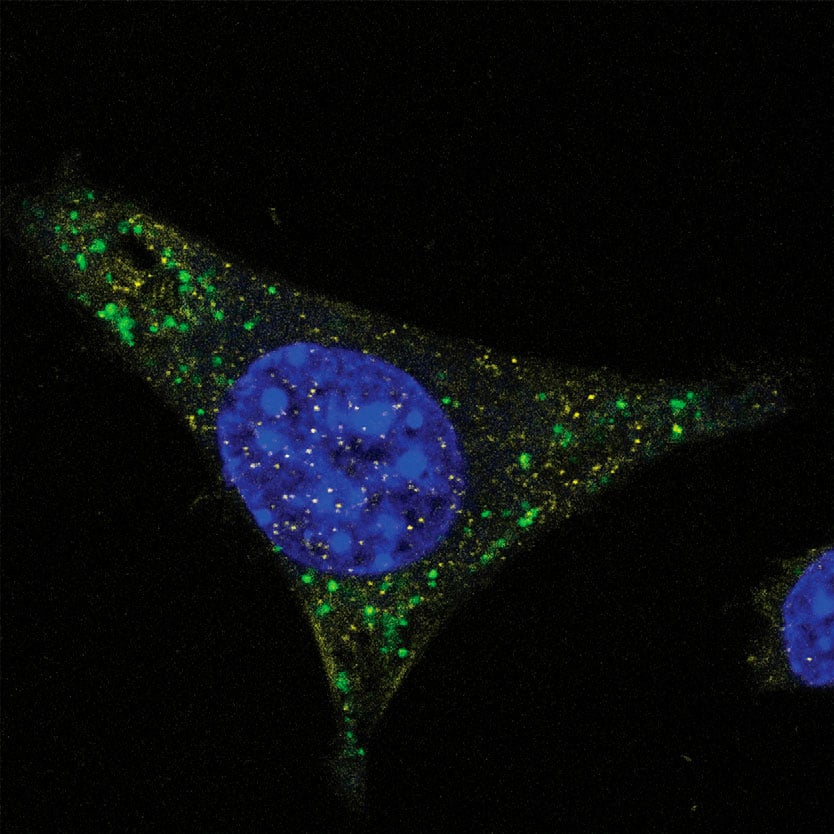
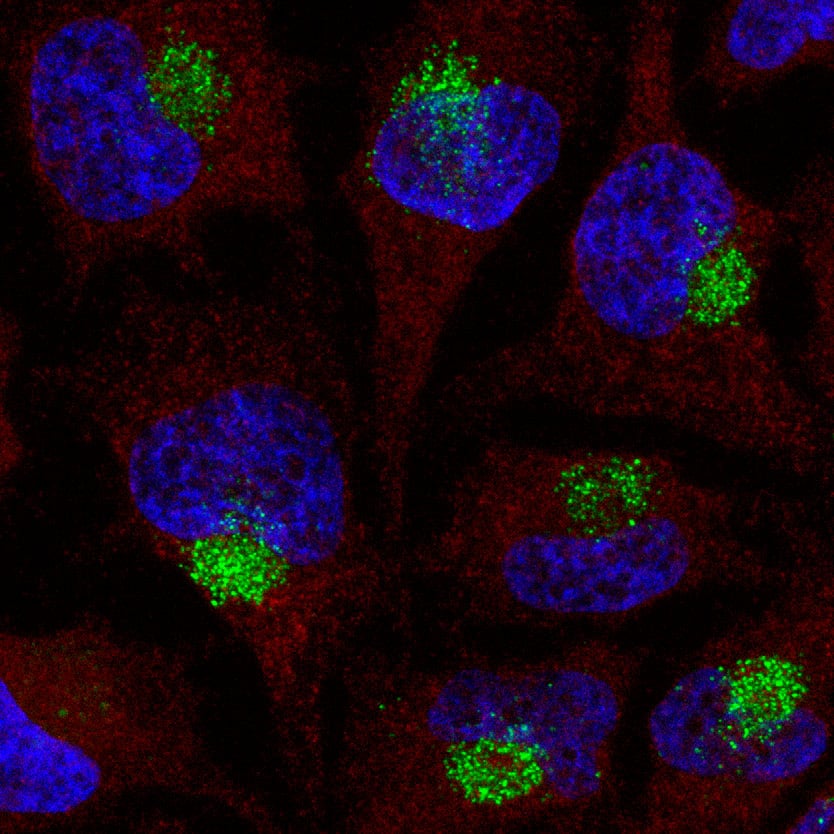
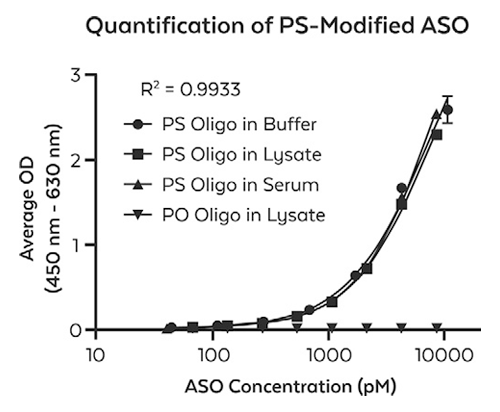
ModDetect™ Panels
ModDetect recognizes key chemical modifications used to stabilize ONTs, specifically phosphorothioate (PS), 2’-O-methoxy-ethyl (MOE), and 2’-O-methyl (OMe) modifications, with additional targets in development. The data presented in this article demonstrate ONT localization and quantification using these antibodies and explore their potential applications in anti-drug assays (ADA), stereochemistry studies, and 3D cell culture studies. Utilizing this technology as an orthogonal approach to existing analytical assays could accelerate drug development and regulatory approvals.
Subcellular Markers for Co-Localization Studies
Co-localization studies are essential for investigating the spatial relationships between molecules within cells. Pairing ModDetect™ with subcellular markers enables precise identification of the compartments where novel RNA therapeutics localize. This approach offers valuable insights into cellular pathways, molecular trafficking, and structural organization.
Explore a curated selection of high-quality subcellular marker products on antibodies-online.com:
Interested in our ModDetect™ product line?
We can help move your program forward—contact us to find out how.