In recent years, extensive research has shed light on the pathological changes that occur in adipose tissue, particularly in obesity. Adipose tissue, which primarily functions as the body’s energy reservoir by storing neutral triglycerides, also acts as an endocrine organ. It produces and releases active biomolecules, known as adipokines, that are involved in a wide range of physiological processes, including energy homeostasis, glucose metabolism, lipid metabolism, feeding behavior, and immune regulation. A major alteration in obesity is the dysregulation of adipokine production (See figure). To date, over 600 adipokines have been identified.1
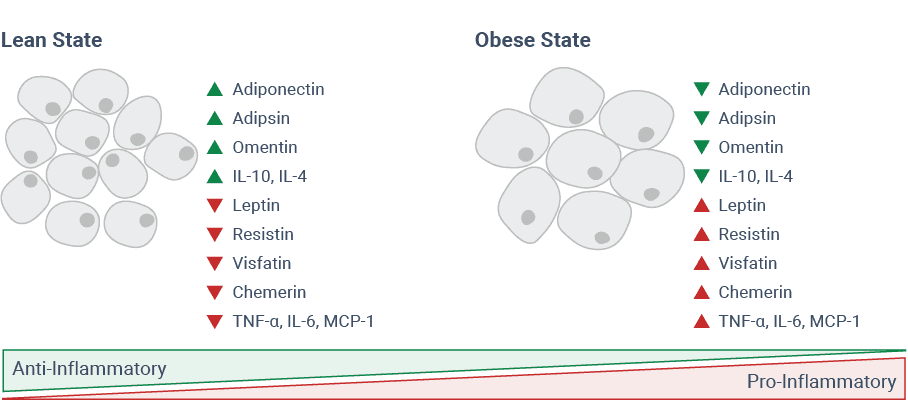
Figure. Adipokines in lean and obese states (Adapted from Taylor, 2021)
Disruptions in adipokine secretion are largely responsible for the prevalence of numerous diseases common in Western societies, such as cancer, type 2 diabetes, hypertension, fatty liver disease, and atherosclerosis. Adipokines also play a role in neuropsychiatric disorders, including depression, anxiety, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, as well as eating disorders.2
Select Adipokines
Leptin
Among adipokines, leptin is perhaps the most studied. Discovered in 1994, leptin is the product of the ob gene in mice and the lep gene in humans.1 Leptin helps to regulate body weight by decreasing appetite and increasing energy expenditure through its interaction with the long form of the leptin receptor (LEPR-B), which activates several signaling pathways, such as the JAK-STAT pathway, PI3K/AKT signaling, MAPK pathway, and AMPK.3 Apart from its role in energy regulation, leptin exhibits pro-inflammatory properties, enhancing the production of cytokines like IL-6, IL-12, IL-18, and TNF-α. Interestingly, studies have observed a link between lower circulating leptin levels and depression, with some clinical trials suggesting that leptin administration may alleviate depressive symptoms.2
Adiponectin
Adiponectin is the most abundant adipokine found in the bloodstream, but its levels are inversely related to body mass index (BMI), triglyceride levels, and insulin resistance.1 Adiponectin serves as an endogenous insulin sensitizer, acting on organs like the liver and skeletal muscle, thus enhancing insulin sensitivity. It also possesses anti-inflammatory and pro-inflammatory properties, demonstrating its dual role in immune regulation. Research in animal models has shown that recombinant adiponectin can lower blood glucose levels and reverse insulin resistance in obese mice.4 Adiponectin plays a role in regulating lipid metabolism, inflammation, and glucose homeostasis.
Resistin
Resistin, another key adipokine, was initially identified as an adipocyte-derived protein linked to insulin resistance in obese mice. Resistin contributes to the impairment of insulin receptor regulation and signaling in adipocytes by activating SOCS3. It is also implicated in promoting inflammation, driving the production of cytokines like IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, TNF-α, and MCP-1, and triggering NF-κB signaling.2 In addition, resistin is released from epicardial adipose tissue and has been associated with systemic inflammation, insulin resistance, and inflammatory pathways.
Chemerin
Chemerin, another adipokine, plays a role in adipogenesis, angiogenesis, and inflammation. Chemerin is a chemokine derived from inflammatory cells, structurally and evolutionarily related to proteins such as cathelicidin precursors (antibacterial peptides), cystatins (inhibitors of cysteine proteases), and kininogens.5 Elevated chemerin levels have been associated with increased cardiovascular risk and severity of coronary artery disease, possibly due to chemerin’s role in endothelial dysfunction and increased arterial stiffness.6
Visfatin
Visfatin, also known as nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (Nampt) or pre-B cell colony-enhancing factor (PBEF), is encoded by the NAMPT gene. High visfatin levels are correlated with obesity and, more specifically, visceral fat accumulation. Like other adipokines, visfatin exerts pro-inflammatory, proliferative, anti-apoptotic, and proangiogenic effects. Elevated plasma visfatin levels have also been linked to various cancers, including colorectal and breast cancer.2
The detection and analysis of adipokines is critical for understanding their roles in health and disease. Antibodies play a crucial role in adipokine research. Monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies are used for the specific detection of adipokines in various assays, including ELISA and Western blot. These methods enable researchers to identify adipokines as potential diagnostic biomarkers for conditions such as obesity, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, autoimmune diseases, and inflammatory diseases.
Adipokine Antibodies
| Product | Clonality | Reactivity | Applications |
| Adiponectin Antibody | Polyclonal | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, ELISA, IHC |
| Adiponectin Antibody | Polyclonal | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, ELISA, IHC, IF |
| Apelin Antibody | Polyclonal | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB |
| CTRP1 Antibody | Polyclonal | Human, Mouse | WB, ELISA |
| CTRP1 Antibody | Polyclonal | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, ELISA, IHC, IF |
| CTRP2 Antibody | Polyclonal | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, ELISA, IHC, IF |
| CTRP2 Antibody | Polyclonal | Human, Mouse | WB, ELISA, IHC |
| CTRP2 Antibody | Polyclonal | Human, Mouse | WB, ELISA |
| CTRP3 Antibody | Polyclonal | Human, Mouse | WB, ELISA, IHC, IF |
| CTRP4 Antibody | Polyclonal | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, ELISA, IHC, IF |
| CTRP4 Antibody | Polyclonal | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, ELISA, IHC, IF |
| CTRP5 Antibody | Polyclonal | Human | WB, ELISA |
| CTRP5 Antibody | Polyclonal | Human, Rat | WB, ELISA, IHC |
| CTRP6 Antibody | Polyclonal | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, ELISA, IHC, IF |
| CTRP6 Antibody | Polyclonal | Human, Mouse | WB, ELISA, IHC, IF |
| CTRP7 Antibody | Polyclonal | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, ELISA, IHC |
| CTRP7 Antibody | Polyclonal | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, ELISA, IHC, IF |
| CTRP7 Antibody | Polyclonal | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, ELISA, IHC |
| Leptin Antibody | Polyclonal | Human, Mouse | WB, ELISA |
| Leptin Antibody | Polyclonal | Human, Mouse | WB, ELISA |
Adipokine Proteins
| Product | Reactivity | Applications |
| rHuman Chemerin Protein | Human | SDS-PAGE |
| rHuman Resistin Dimer Protein | Human | SDS-PAGE, Cellular Assay |
| rHuman Visfatin Protein | Human | SDS-PAGE, Cellular Assay |
Adipokine ELISA Kits
| Product | Reactivity | Applications |
| Human Chemerin - RARRES2 ELISA Kit | Human | ELISA |
| Mouse Chemerin - RARRES2 ELISA Kit | Mouse | ELISA |
| Human FSTL1 ELISA Kit | Human | ELISA |
| Human Lipocalin-2 - NGAL ELISA Kit | Human | ELISA |
| Mouse Lipocalin-2 - NGAL ELISA Kit | Mouse | ELISA |
| Rat Lipocalin-2 - NGAL ELISA Kit | Rat | ELISA |
| Human Nesfatin-1 ELISA Kit | Human | ELISA |
| Human PAI-1 ELISA Kit | Human | ELISA |
| Human Progranulin ELISA Kit | Human | ELISA |
| Mouse Progranulin ELISA Kit | Mouse | ELISA |
| Human RBP4 ELISA Kit | Human | ELISA |
| Mouse RBP4 ELISA Kit | Mouse | ELISA |
| Human Resistin ELISA Kit | Human | ELISA |
| Human SPARC ELISA Kit | Human | ELISA |
| Human WISP1 - CCN4 ELISA Kit | Human | ELISA |
| Mouse WISP1 - CCN4 ELISA Kit | Human | ELISA |