Single B Cell Cloning
Single B Cell Cloning
Rockland leverages single B cell cloning to generate high-quality recombinant antibodies (rAbs). This technique involves isolating individual B cells from peripheral blood or lymphoid tissues using methods such as fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS). By maintaining the natural VH and VL pairing found in B cells, this method ensures that the functional specificity and affinity of the antibodies are preserved. By integrating single B cell cloning into our recombinant antibody workflow, we can offer a highly efficient method to generate functional rAbs for research, diagnostic, and therapeutic applications.
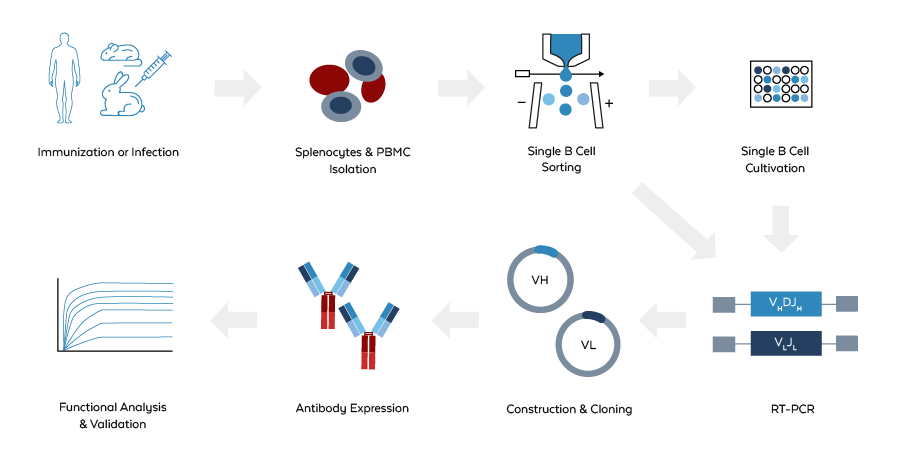
Figure. Generation of recombinant antibodies using single B cell cloning technology
Our Single B Cell Cloning Workflow
Immunization or Screening
An immune-reactive subject is either immunized with a target antigen or screened for existing immune responses.Isolation of Immune Cells
Immune cells, including antigen-specific B cells, are harvested from the spleen, blood, or lymph nodes.Sorting of B Cells
Single B cells are sorted using flow cytometry based on specific markers and antigen binding, such as CD19 for B cells and CD27 for memory B cells.Cultivation and Testing
The sorted B cells are cultured, and their antibody production is tested.Amplification of Variable Regions
The variable regions of the heavy (VH) and light (VL) chains of the mRNA are amplified using RT-PCR.Cloning
The amplified VH and VL gene sequences are cloned into expression vectors.Transfection
The vectors are transfected into host cells to produce recombinant antibodies.Validation
The specificity and functionality of the antibodies are validated using functional assays such as Bio-Layer Interferometry (BLI).Interested in single B cell cloning?
Talk with us to find out how we can help move your research forward.