Anti-Oligonucleotide Antibodies
Anti-Oligonucleotide Antibodies
Advance your anti-oligonucleotide antibody therapeutic or vaccine development program with highly specific and sensitive antibodies generated by the proven anti-modified oligonucleotide antibody experts at Rockland.
We have a demonstrated history of successful generation of antibodies, including polyclonals, conventional monoclonals, and recombinant monoclonals. Antibodies can be raised against different types of nucleic acid targets, such as antisense oligonucleotides, modified mRNA, ssDNA, DNA:RNA hybrids, and modified phosphate backbones and nucleosides. Rockland’s scientists can customize an anti-oligonucleotide antibody generation project for your program’s needs and specific application.
Custom Antibodies to Nucleic Acids
We are experienced in working with a variety of chemistries, including:
Our Oligonucleotide Antibody Production Process
Each oligonucleotide antibody production project typically includes four phases: antigen preparation, antibody development, purification, and characterization.
The below graph depicts the timeline of an oligonucleotide antibody production case study; however, your timeline can vary depending on the specific needs of your project.
| Months | ||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |
| Antigen Preparation | ||||||||
| Antibody Development | ||||||||
| Antibody Purification | ||||||||
| Antibody Characterization | ||||||||
Phase 1: Antigen Preparation
We work closely with you to understand the biochemical properties of the target nucleic acid antigen and are experienced working with a variety of chemistries, including:
- Conventional oligonucleotides (12-15 bases)
- DNA-RNA hybrids
- Modified oligonucleotide with phosphorothiorate (PS) and phosphorodithioate (PdiS) modified backbones
- Single stranded oligonucleotide mixtures (cocktails)
- Single stranded RNA (ssRNA)
- Double stranded RNA (dsRNA)
- Nucleotides
- Nucleosides
Because nucleic acids by themselves are notoriously poor immunogens and are difficult to use as an analyte in immunoassays, we have developed and optimized a number of different conjugation methods that enhance the immunogenicity of the target nucleic acid.
Our conjugation methods lead to highly efficient presentation of the oligonucleotide to the host immune system, resulting in antibodies that specifically recognize backbone-specific nucleic acids (e.g. phosphorothioate) and/or compositions (i.e. RNA-DNA hybrids).
In addition to serving as an immunogen, the conjugated target nucleic acid is also a highly effective reagent for screening immunoassays and clonal selection.
Phase 2: Anti-Oligonucleotide Antibody Development
For anti-oligonucleotide polyclonal antibody generation, we will recommend a host, immunization protocols, and testing strategies. We also purify the antibody, enhance specificity by cross adsorption, and validate performance using predetermined criteria we establish with you at the start of the project.
For conventional monoclonal and recombinant antibody generation, we will recommend the clonal cell lines that yield antibody reagents with the desired performance characteristics such as sensitivity, specificity, yield, and affinity.
Phase 3: Antibody Production and Purification
We can produce and purify your anti-oligonucleotide antibody using a number of methods, depending on whether we are generating a polyclonal, conventional monoclonal, or recombinant antibody.
Rockland's production capabilities allow for variable manufacturing batch sizes, from small scale pilot batches to large scale manufacturing lots using roller bottle cultures or large animal antisera pools.
Purification options for polyclonals, monoclonals, and recombinants:
- Protein A purification
- Protein G purification
- Protein A/G purification
- Epitope-tag purification
Phase 4: Antibody Characterization and Validation
The specificity and sensitivity of anti-oligonucleotide antibodies produced at Rockland can be characterized using a number of different immunoassays, including IHC for biodistribution, IF for intracellular localization, and ELISA for anti-drug antibody (ADA) assays. When producing fit-for-purpose antibodies, we validate performance using the intended assay.
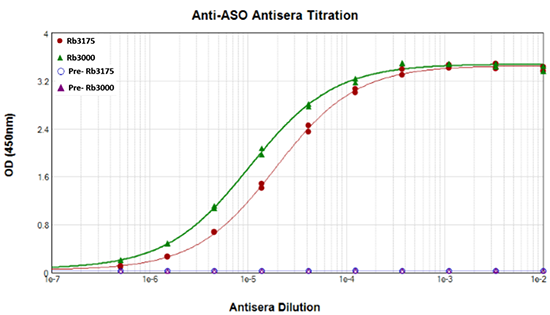
Figure 2. An example characterization of an anti-oligonucleotide antibody that was intended for use in an ELISA. Antisera from rabbits immunized with oligonucleotide cocktail was added in increasing amounts to ELISA plates coated with carrier-conjugated antigen. Both pre-bleeds from the rabbits confirm the hosts were not previously exposed to the antigen.
Interested in anti-oligo antibody production?
Talk with us to find out how we can help move your research forward.